Milling Services
Milling Services
Milling is one of the most versatile machining processes, essential for producing parts with complex shapes, precise dimensions, and high-quality finishes. Our milling services use advanced technology to meet the demands of industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and energy. This catalogue provides an in-depth look at the different types of milling processes we offer, including the machines used, capabilities, and typical applications.
Materials Processed:
- Metals: Stainless steel (SS316, SS304), Carbon steel, Aluminum, Titanium, Brass, Copper, Inconel, Tool steels, and Alloys
- Plastics: PEEK, PTFE, Delrin, ABS, Nylon, Polycarbonate
- Exotic Materials: High-temperature alloys, Ceramics, and Composites
- ∙ Maximum Workpiece Size: 1,500 mm x 1,500 mm
- Maximum Weight: Up to 1,000 kg
- Tolerance Accuracy: ±0.005 mm
- Low to High-Volume Production: From prototype and small batches to large-scale production runs
- Surface Finish: As fine as 0.2 µm Ra
- Complexity: Capable of both simple and highly intricate parts with tight tolerances Types of
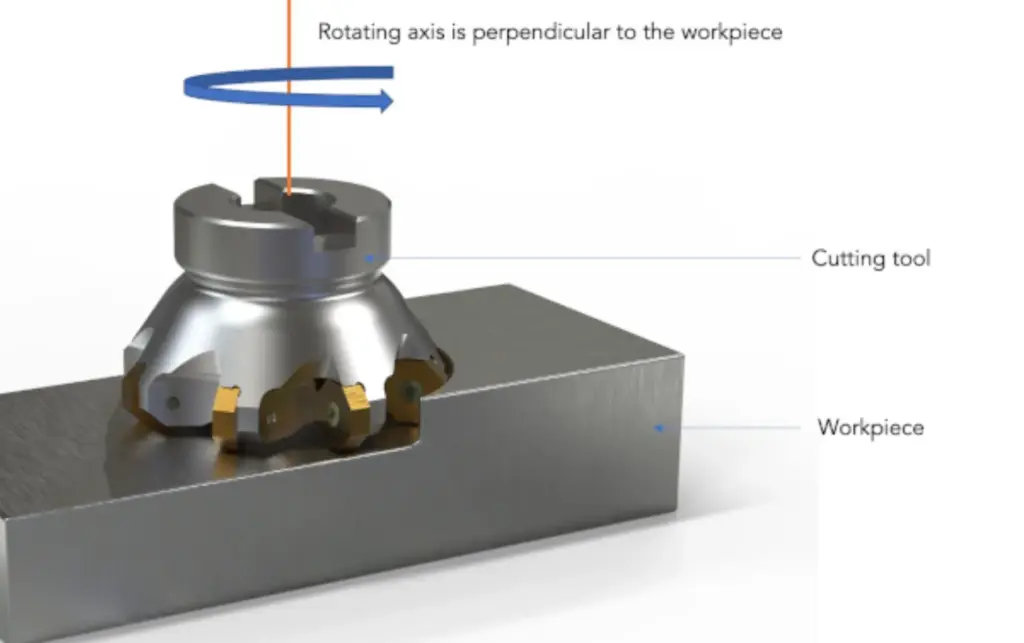
Milling Processes and Capabilities
Face Milling
Process Description: Face milling is a process where the cutting tool primarily removes material from the surface of the workpiece. The cutting tool’s face is the active part, and it is used to create a smooth, flat surface.
Machines Used:
- CNC Vertical Milling Machines: For precision face milling with automated control. ∙
- CNC Horizontal Milling Machines: Used for larger workpieces or for simultaneous multi-face milling.
Applications:
Shafts, rods, and cylindrical components
Parts requiring high dimensional accuracy and smooth finishes
Key Features:
High tolerance and surface finish
Uniform diameter along the length of the workpiece
Taper Turning
Process Description:
Taper turning involves gradually reducing the diameter of a workpiece from one end to the other to create a conical shape. This can be achieved by tilting the cutting tool or adjusting the lathe settings to control the taper angle.
Machines Used:
- CNC Lathes: For precise control of taper angles and lengths.
- Manual Lathes with Taper Attachments: Suitable for simpler, small-volume tasks where the taper angle is not complex.
Applications:
Flat surfaces on parts such as engine blocks, plates, and housings.
Creating smooth surfaces for component assembly.
Key Features:
- High-quality surface finish.
- Precise control over surface flatness and dimension.
- Capable of handling large or small workpieces.
End Milling
Process Description: End milling involves using a rotating tool with cutting edges on both the side and the end to cut material. It is suitable for producing slots, pockets, and profiles on the workpiece.
Machines Used:
CNC Milling Machines: With end mills for high-precision and multi-axis machining.
Manual Milling Machines: For simpler, low-volume tasks requiring smaller cuts.
Applications:
- Creating slots, keyways, and contours.
- Machining complex shapes such as gears and turbine blades.
Key Features:
- High precision in both vertical and horizontal directions.
- Ability to handle both small and large cutting tasks.
- Versatile in terms of cutting geometries.
Slot Milling
Process Description: Slot milling is used to create slots or grooves in the workpiece. It typically uses a tool with multiple cutting edges along its side to create narrow channels.
Machines Used:
CNC Milling Machines: Equipped with high-precision tools to create narrow and deep slots.
Manual Milling Machines: For simple tasks with small slots.
Applications:
Keyways, grooves for inserts, or channels for assembling parts.
Parts for automotive, aerospace, and heavy machinery.
Key Features:
High accuracy for slot depth and width.
Suitable for both straight and curved slots.
Profiling
Process Description: Profiling is a milling process used to create complex, contoured shapes along the surface of the workpiece. It is often used for parts with intricate designs and varying depths.
Machines Used:
5-Axis CNC Milling Machines: These machines can move the tool in multiple directions to create complex contours.
CNC Vertical and Horizontal Milling Machines: For less intricate but still precise profiles.
Applications:
Aerospace and automotive components with complex geometries.
Mold and die production, such as for plastic injection molds.
Key Features:
Capable of creating highly intricate and curved geometries.
High precision for complex, multi-dimensional profiles.
Drilling and Reaming
Process Description: While drilling creates circular holes, reaming is used to finish the holes to a precise diameter and high surface finish. This process is critical for parts that require tight hole tolerances.
Machines Used:
CNC Milling Machines with Drilling Capabilities: These machines can switch between drilling and reaming operations.
Radial Drilling Machines: For larger or deeper holes that require a stationary workpiece.
Applications:
Producing mounting holes for fasteners, pins, or screws.
Holes for bearings, valves, and critical aerospace components.
Key Features:
High precision in hole diameter and alignment.
Ability to handle deep and small-diameter holes.
Contour Milling
Process Description: Contour milling is used to create curved profiles on the workpiece surface. The cutting tool follows a pre-programmed path to achieve complex, curved edges.
Machines Used:
5-Axis CNC Milling Machines: Essential for achieving high-precision contours in multiple directions.
- CNC Horizontal Milling Machines: Used for larger parts with curved surfaces.
Applications:
Automotive, aerospace, and medical components with complex surfaces.
Parts for molds and dies with curved features.
Key Features:
High precision for creating intricate contours.
Capable of handling both shallow and deep curves.
Pocket Milling
Process Description: Pocket milling is used to create cavities or pockets in a part’s surface, typically with a flat bottom. It involves the tool moving in and out of the workpiece to remove material efficiently.
Machines Used:
CNC Milling Machines: Automated pocket milling for high efficiency and precision. ∙
Manual Milling Machines: For smaller pockets or less complex designs.
Applications:
Manufacturing pockets for inserts, tools, and valve bodies.
Aerospace and automotive components that require material removal from within the part.
Key Features:
High efficiency in material removal.
Ability to create deep pockets with high precision.
Tapping
Process Description: Tapping is used to create internal threads within a hole. A tap tool is used to cut the threads, providing a surface for screws or bolts to be screwed into.
Machines Used:
CNC Milling Machines with Tapping Capabilities: Used for automated tapping of holes with precise thread pitches.
Manual Milling Machines: For simpler tapping tasks with lower volume.
Applications:
Production of threaded holes for fasteners, screws, and bolts.
Aerospace, automotive, and construction parts requiring thread accuracy.
Key Features:
High accuracy in thread pitch and depth.
Suitable for various thread sizes and materials.
Machines Used for Milling Processes
We use a range of advanced machinery to ensure the highest standards of precision and quality in milling operations:
- CNC Milling Machines (3-Axis, 4-Axis, and 5-Axis): Automated, multi-axis machines that allow for complex geometries, intricate details, and fast production.
- Vertical and Horizontal Milling Machines: For operations requiring precision on both sides of the workpiece or for parts with multi-faceted surfaces.
- Bridge Mills: Large-scale machines capable of handling oversized parts with high precision.
- Knee Mills and Turret Mills: For smaller, simpler milling tasks or when manual control is required.
- High-Speed Machining Centers: For operations requiring high-speed cutting and fine surface finishes, particularly for intricate components in the aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors.
